The Dow Jones index is price-weighted, meaning that companies with higher prices influence the index the most. For example, Boeing used to have the most significant impact on the Dow Jones index, when it was trading above 400 USD as it was the most expensive stock in the index. Nowadays, the price has dropped below 200 USD. Thus the significance of Boeing in Dow Jones has lessened significantly.
For this reason (price-weighting), traders usually don’t take the Dow Jones index as an investing benchmark, and neither economists track this index when comparing the US economy with US stocks. Commonly, the SP500 index is chosen as a benchmark due to its broadest portfolio of stocks, representing each sector of the US economy.
Two Dow Jones indices
There are two Dow Jones indices – one is the mentioned Industrial Average, and the second, less known, is the Transportation Average. The transportation average index tracks mostly transportation companies, such as railroads, freighters, trucking, etc.
Calculation
To calculate the Dow Jones Index, the sum of the prices of all 30 stocks is divided by a divisor, the Dow Divisor. The divisor is adjusted in case of stock splits, spinoffs, or similar structural changes to ensure that such events do not in themselves alter the numerical value of the DJIA. The mentioned divisor is currently around 0.1458.
As previously said, if investors and traders want exposure to the whole US market, they don’t trade the Dow Jones as it contains only 30 largest companies in the USA, without a serious sector diversification. In this case, traders often trade the SP500 index.
Performance
As the other three US indices, the DJIA has gone nowhere but up since the financial crisis.
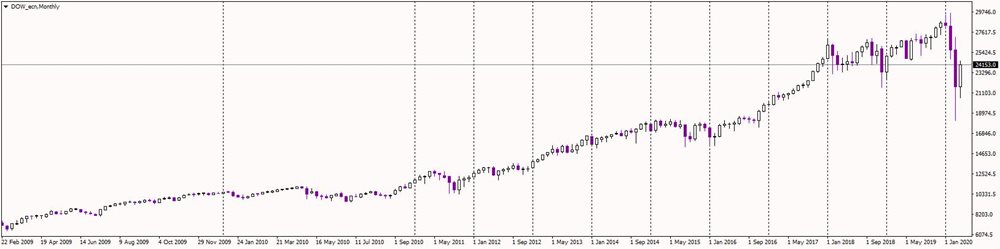
Source: Purple Trading Metatrader 4
The monthly chart shows that if a correction occurred, it was usually only a small one and shortly afterward, the market rallied to new cycle highs.
The DJIA is volatile and liquid enough for short-term traders, but long-term investors tend to prefer the SP500 index, due to its broad sector diversification. However, investing into DJIA can be equally rewarding.
Over the long-term, US equities always go up. But sometimes the timing is crucial, so be careful when trading/investing.
Composition of the index
As of 2020, there are following companies in the Dow Jones index:
|
Company
|
Industry
|
Index weighting (march, 2020)
|
|
3M
|
Conglomerate
|
4.34%
|
|
American Express
|
Financial services
|
2.75%
|
|
Apple Inc.
|
Information technology
|
8.08%
|
|
Boeing
|
Aerospace and defense
|
4.18%
|
|
Caterpillar Inc.
|
Construction and Mining
|
3.31%
|
|
Chevron Corporation
|
Petroleum industry
|
2.18%
|
|
Cisco Systems
|
Information technology
|
1.26%
|
|
The Coca-Cola Company
|
Food industry
|
1.29%
|
|
Dow Inc.
|
Chemical industry
|
0.93%
|
|
ExxonMobil
|
Petroleum industry
|
1.16%
|
|
Goldman Sachs
|
Financial services
|
5.02%
|
|
The Home Depot
|
Retailing
|
6.04%
|
|
IBM
|
Information technology
|
3.45%
|
|
Intel
|
Information technology
|
1.71%
|
|
Johnson & Johnson
|
Pharmaceutical industry
|
3.90%
|
|
JPMorgan Chase
|
Financial services
|
2.89%
|
|
McDonald's
|
Food industry
|
5.30%
|
|
Merck & Co.
|
Pharmaceutical industry
|
2.26%
|
|
Microsoft
|
Information technology
|
4.85%
|
|
Nike
|
Apparel
|
2.36%
|
|
Pfizer
|
Pharmaceutical industry
|
0.97%
|
|
Procter & Gamble
|
Fast-moving consumer goods
|
3.38%
|
|
Raytheon Technologies
|
Aerospace and defense
|
2.84%
|
|
The Travelers Companies
|
Financial services
|
3.07%
|
|
UnitedHealth Group
|
Managed health care
|
7.19%
|
|
Verizon
|
Telecommunication
|
1.64%
|
|
Visa Inc.
|
Financial services
|
5.05%
|
|
Walmart
|
Retailing
|
3.76%
|
|
Walgreens Boots Alliance
|
Retailing
|
1.48%
|
|
The Walt Disney Company
|
Broadcasting and entertainment
|
3.21%
|